Python for Excel
Overview
The Python for Excel Add-in lets you create reusable custom Excel functions using Python code. Write a function once, use it anywhere in your workbook.
Quick Example:
- Write a Python function:
def hello(name):
""" Returns a greeting. """
return f"Hello {name}!"- Use it in Excel:
=HELLO("World")Feature:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| ✅ Custom Functions | Write Python functions and use them in Excel |
| 🆓 Free | Unlimited free use |
| 🌐 Cross-Platform | Works in Excel for web and desktop |
| ☁️ Network Access | Make API calls from your functions (supports CORS) |
| 📦 Packages | Import standard library and pure Python packages |
| 🔒 Private | Code is stored in your workbook and runs locally in the browser |
Your Python code must be a function. This add-in does not work the same way as Excel’s native =PY() function.
Excel has a built-in =PY() function. Here’s when to use each:
| Feature | This Add-in | Native =PY() |
|---|---|---|
| Reusable functions | ✅ Create =FUNCTION_NAME() |
❌ Code in each cell |
| Runs where | Browser (local) | Microsoft Cloud |
Getting Started
- Install the add-in from Microsoft AppSource
- Sign in with your current Microsoft account when prompted
- Grant permissions for the add-in to function
- Open the Editor tab (✏️) to write your first function
- Save your function and use it as
=FUNCTION_NAME()
You can type functions directly into cells (for example, =HELLO("World")) or use the Function Dialog for a guided experience.
Note: Built-in example functions (
BF.*) are loaded when you first insert them using the Function Insert tab. This improves performance since there are hundreds of them.
Python Editor
The Editor tab (✏️) is where you write and manage your custom functions.
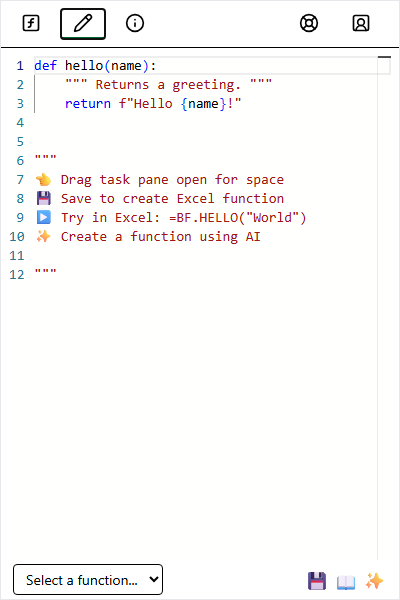
Write standard Python code, must be a function.
Writing a Function
def my_function(arg1, arg2):
"""
Description for the function wizard.
"""
return arg1 + arg2| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Arguments | arg1, arg2, etc. correspond to Excel inputs |
| Return | The value returned becomes the cell value (number, text, or matrix) |
Type Conversion
Excel types are automatically converted to Python types and vice versa.
Excel → Python
| Excel Type | Example | Python Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 42 or 3.14 |
float |
All numbers become floats, even integers |
| String | "hello" |
str |
|
| Boolean | TRUE |
bool |
|
| Empty Cell | None |
||
| Date | 45678 |
float |
Excel stores dates as serial numbers* |
| Range | A1:B2 |
list[list] |
Always 2D, e.g., [[1, 2], [3, 4]] |
*To convert an Excel date serial to Python datetime:
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
def excel_date_to_datetime(serial):
return datetime(1899, 12, 30) + timedelta(days=serial)Python → Excel
| Python Type | Example | Excel Result |
|---|---|---|
int/float |
42, 3.14 |
Number |
str |
"hello" |
String |
bool |
True |
TRUE |
None |
None |
Empty cell |
datetime |
datetime(2022, 1, 1) |
Date (serial) |
list[list] |
[[1,2],[3,4]] |
Spill range |
Importing Packages
The add-in uses Pyodide (Python in the browser). Many scientific packages like pandas, numpy, and scipy are included in the distribution and can be simply imported.
Other pure Python packages can be installed using Micropip from PyPI:
import micropip
await micropip.install(['textdistance', 'faker'])
import textdistance
# ...Package installation only works if the package and all its dependencies are pure Python. For example, yfinance fails with ValueError: Can't find a pure Python 3 wheel for 'curl-cffi>=0.7' because it depends on curl-cffi, which has C-extensions.
Limitations
| Limitation | Workaround |
|---|---|
| No local file access (browser security) | Use Excel’s Power Query to import files first, or fetch from a URL |
No *args or **kwargs |
Define explicit parameters for each argument |
| Limited networking (CORS only) | Use public APIs or set up a CORS proxy for private APIs |
Managing Functions
| Action | How To |
|---|---|
| Save | Click Save. Function becomes available as =FUNCTION_NAME() |
| Delete | Click ❌. Removes the function from the workbook |
| Edit | Select a function from the dropdown list |
| New | Select “Select a function…” or clear the editor |
Insert Function
The Insert Function tab provides a guided experience for finding and inserting functions similar to Excel’s native function dialog. You can use it to insert custom functions you create, or built-in example functions. As noted earlier, the built-in example functions have a BF. prefix.
Select Function
Use the search box or category dropdown to find a function.

Search for a function. Functions with a BF. prefix are built-in example functions. Functions without a prefix are custom functions you create.
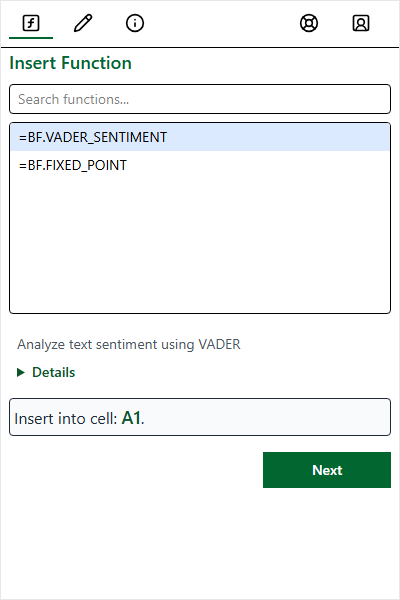
Click a function to see its description and details. Click Next to proceed to the argument entry screen.
Enter Arguments
Enter values for each argument. A preview on the right shows how the value is interpreted.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Type Value | Enter numbers, text, or booleans directly |
| Select Range | Click the input field, then select cells in Excel. Displays as Sheet1!A1:B2 |
| Test Values | Click Use Test Values to fill all fields with sample data |
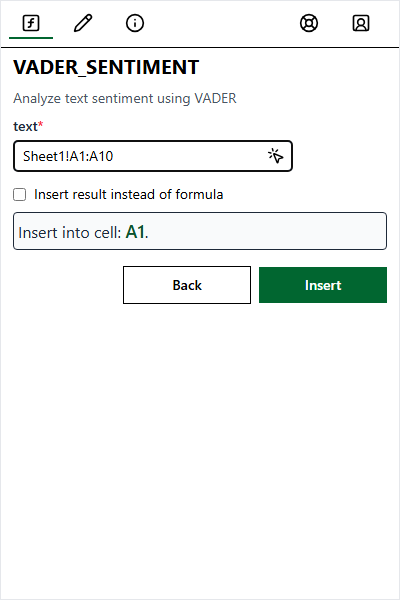
Click into an input field to activate selection mode, then highlight cells in your sheet.
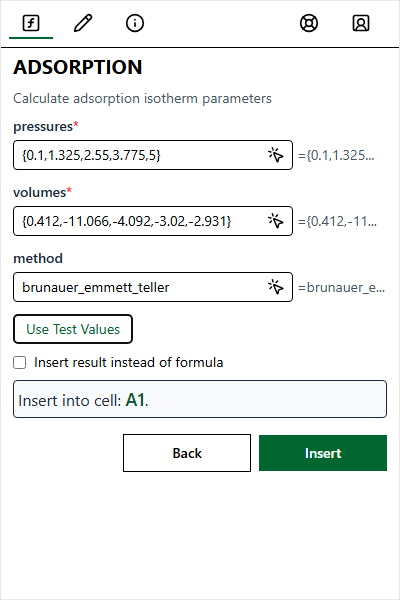
See exactly what data will be passed to Python (e.g., matrices for ranges).
Insert Options
Before clicking Insert, choose how the result should appear:
| Option | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Insert as Formula (Default) | Inserts =FUNCTION_NAME(arg1, arg2). Recalculates when inputs change. |
Most use cases |
| Insert as Result | Inserts the static calculated value (e.g., 42). Check “Insert result instead of formula”. |
One-time calculations or breaking dependencies |
| Insert as Excel PY | Inserts =PY("...", 0) using Excel’s native Python runtime. Check “Insert =PY() formula”. |
Leveraging Excel’s built-in Python environment |
Note: The Excel PY option only appears for functions compatible with Excel’s Python environment.
Info Tab
The Info tab (ℹ️) displays print() output and error tracebacks (STDOUT and STDERR).
View print() output and error tracebacks here. Useful for debugging.
FAQ
Why is my function slow the first time?
The first call to any function imports libraries and initializes the Python runtime. Subsequent calls are much faster.How do I debug my function?
Addprint() statements to your code. Output appears in the Info tab (ℹ️) after the function finishes executing.
Where is my code stored?
Your custom functions are saved directly into the Excel workbook’s metadata. They travel with the file, so any user with the workbook can use them after installing the add-in.Where does print() output go?
Output fromprint() and errors appear in the Info tab (ℹ️) of the taskpane. Note that output only appears after the function finishes executing.
Can I use this offline?
No, the add-in requires an internet connection to load the Python runtime and libraries.Where are OneDrive sync files?
This feature has been removed, but the files are still stored in your OneDrive atMy Files > Apps > Boardflare Python for Excel.
#VALUE! Error
This error occurs when an argument has the wrong type or is missing.
Common causes: - Passing text where a number is expected - Referencing a range with incompatible data types - Missing required arguments
Solution: Check that all arguments are provided and have the correct type.#NAME? Error
This error appears when Excel doesn’t recognize the function name.
Common causes: - Function name is misspelled - Add-in hasn’t fully loaded yet - Function was never saved (check the Editor tab)
Solution: Verify the spelling and prefix. Wait a few seconds for the add-in to load. Open the taskpane to ensure the add-in is active.#BUSY! Error
This is usually temporary and indicates processing.
Common causes: - First-time import of libraries (can take 5-10 seconds) - Slow internet connection - Function is still calculating
Solution: Wait a few seconds. If it persists, click Reset in the Info tab.