Compressible
Overview
Compressible flow describes fluid motion where density changes are significant—typically when gas velocities approach or exceed the speed of sound. Unlike incompressible flow where density remains constant, compressible flow exhibits complex coupling between velocity, pressure, temperature, and density through thermodynamic relationships. This behavior dominates in high-speed aerodynamics, gas pipeline networks, turbomachinery, and rocket nozzles.
The defining characteristic of compressible flow is the Mach number, M = V/c, where V is flow velocity and c is the local speed of sound. When M < 0.3, density changes remain below 5% and incompressible assumptions suffice. As Mach number increases, compressibility effects intensify: shock waves form, flow can become choked (reaching sonic conditions), and thermodynamic processes dictate pressure-temperature relationships.
Implementation: These tools leverage thermodynamic calculations through SciPy for property evaluation and implement classical gas dynamics correlations for pipeline flow. The tools handle both idealized thermodynamic processes (isentropic, isothermal, polytropic) and practical empirical formulas developed for natural gas transmission.
Thermodynamic Processes govern how gases behave during compression, expansion, and flow through varying areas. Isentropic processes assume reversible adiabatic conditions—ideal for analyzing turbomachinery and nozzles where heat transfer is negligible and losses are small. The ISENTROPIC_WORK, ISENTROPIC_T_RISE, and ISENTROPIC_EFF tools quantify compression work, temperature changes, and efficiency conversions for compressors and turbines. Isothermal processes assume constant temperature—applicable to slow compression with heat removal or long pipelines where gas temperature equilibrates with surroundings. The ISOTHERMAL_WORK and ISOTHERMAL_GAS tools handle these conditions. Polytropic processes represent real compression with some heat transfer, captured by the POLYTROPIC_EXP tool which relates efficiency to the polytropic exponent.
Stagnation Properties measure total energy available in a flow by accounting for both static conditions and kinetic energy. P_STAGNATION and T_STAGNATION convert between static and stagnation states, essential for performance analysis of compressors, turbines, and wind tunnels. The STAGNATION_ENERGY quantifies the enthalpy rise from velocity, while T_STAG_IDEAL provides the theoretical temperature rise.
Critical Flow Conditions occur when flow reaches Mach 1, establishing maximum flow rates that cannot increase regardless of further downstream pressure reduction—a phenomenon called choking. The IS_CHOKED_FLOW tool determines whether flow has reached critical conditions based on pressure ratio, while P_CRITICAL_FLOW and T_CRITICAL_FLOW calculate the exact pressure and temperature at the sonic condition. This behavior governs relief valve sizing, nozzle design, and pipeline capacity limits.
Pipeline Flow Formulas provide empirical correlations for natural gas transmission developed from extensive field data. These formulas account for friction, compressibility, and non-ideal gas behavior in long pipelines. WEYMOUTH_FLOW applies to large-diameter, high-pressure transmission lines with turbulent flow. PANHANDLE_A and PANHANDLE_B suit partially turbulent flow in moderate-diameter lines, with Panhandle B providing better accuracy for modern smooth pipes. FRITZSCHE_FLOW, MULLER_FLOW, and IGT_FLOW offer alternative formulations calibrated to specific pipeline conditions and gas properties.
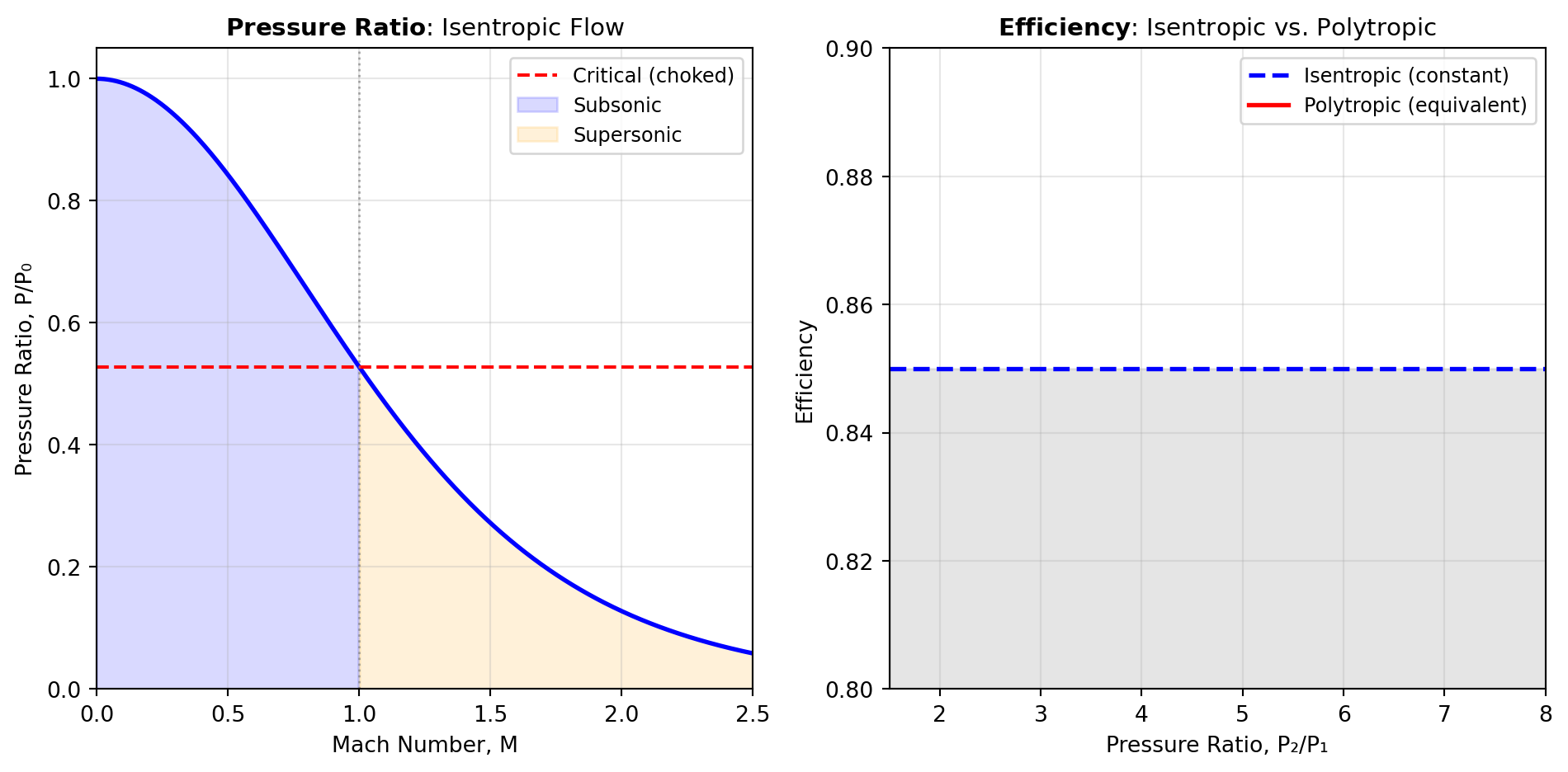
Figure 1 illustrates the relationship between pressure ratio and Mach number in isentropic flow, and the efficiency conversions between isentropic and polytropic processes in compression.

FRITZSCHE_FLOW
This function estimates steady natural-gas pipeline flow at reference conditions using the Fritzsche correlation in SI units. It is commonly used when inlet/outlet pressure, pipe geometry, gas specific gravity, and average temperature are known.
Q \propto \left(\frac{P_1^2-P_2^2}{L\,SG^{0.8587}\,T_{avg}}\right)^{0.538} D^{2.69}
Excel Usage
=FRITZSCHE_FLOW(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor, efficiency)sg(float, required): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]temp_avg(float, required): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]length(float, required): Length of pipe [m]diameter(float, required): Diameter of pipe [m]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Average compressibility factor [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Pipeline efficiency factor [-]
Returns (float): Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
Example 1: Standard natural gas pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.693 | 277.15 | 160000 | 0.34 | 9000000 | 2000000 |
Excel formula:
=FRITZSCHE_FLOW(0.693, 277.15, 160000, 0.34, 9000000, 2000000)Expected output:
39.4215
Example 2: Short pipeline section
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 290 | 10000 | 0.5 | 5000000 | 4500000 |
Excel formula:
=FRITZSCHE_FLOW(0.65, 290, 10000, 0.5, 5000000, 4500000)Expected output:
111.043
Example 3: Pipeline with 92% efficiency
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 280 | 50000 | 0.4 | 7000000 | 3000000 | 0.92 |
Excel formula:
=FRITZSCHE_FLOW(0.7, 280, 50000, 0.4, 7000000, 3000000, 0.92)Expected output:
73.0675
Example 4: Large diameter pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 285 | 100000 | 1 | 8000000 | 4000000 |
Excel formula:
=FRITZSCHE_FLOW(0.6, 285, 100000, 1, 8000000, 4000000)Expected output:
754.802
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import Fritzsche as fluids_fritzsche
def fritzsche_flow(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor=1, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate gas flow rate using the Fritzsche formula.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.Fritzsche
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
sg (float): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]
temp_avg (float): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]
length (float): Length of pipe [m]
diameter (float): Diameter of pipe [m]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
comp_factor (float, optional): Average compressibility factor [-] Default is 1.
efficiency (float, optional): Pipeline efficiency factor [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
"""
try:
sg = float(sg)
temp_avg = float(temp_avg)
length = float(length)
diameter = float(diameter)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if sg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: sg must be positive."
if temp_avg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_avg must be positive."
if length <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: length must be positive."
if diameter <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: diameter must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be non-negative."
if p_outlet >= p_inlet:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be less than p_inlet."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_fritzsche(SG=sg, Tavg=temp_avg, L=length, D=diameter,
P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, Zavg=comp_factor, E=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
IGT_FLOW
This function computes compressible-gas pipeline flow using the IGT empirical correlation with viscosity effects included. It is suitable for steady-state throughput estimation when pressure drop, line geometry, and gas properties are known.
Q \propto \left(\frac{P_1^2-P_2^2}{L\,Z_{avg}\,T_{avg}}\right)^{5/9}\frac{D^{8/3}}{\mu^{1/9}SG^{4/9}}
Excel Usage
=IGT_FLOW(sg, temp_avg, viscosity, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor, efficiency)sg(float, required): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]temp_avg(float, required): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]viscosity(float, required): Average viscosity of gas [Pa·s]length(float, required): Length of pipe [m]diameter(float, required): Diameter of pipe [m]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Average compressibility factor [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Pipeline efficiency factor [-]
Returns (float): Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
Example 1: Standard natural gas pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.693 | 277.15 | 0.00001 | 160000 | 0.34 | 9000000 | 2000000 |
Excel formula:
=IGT_FLOW(0.693, 277.15, 0.00001, 160000, 0.34, 9000000, 2000000)Expected output:
48.9235
Example 2: Short pipeline section
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 290 | 0.000012 | 10000 | 0.5 | 5000000 | 4500000 |
Excel formula:
=IGT_FLOW(0.65, 290, 0.000012, 10000, 0.5, 5000000, 4500000)Expected output:
133.548
Example 3: Pipeline with 92% efficiency
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 280 | 0.00001 | 50000 | 0.4 | 7000000 | 3000000 | 0.92 |
Excel formula:
=IGT_FLOW(0.7, 280, 0.00001, 50000, 0.4, 7000000, 3000000, 0.92)Expected output:
91.1455
Example 4: Large diameter pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 285 | 0.000011 | 100000 | 1 | 8000000 | 4000000 |
Excel formula:
=IGT_FLOW(0.6, 285, 0.000011, 100000, 1, 8000000, 4000000)Expected output:
901.065
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import IGT as fluids_igt
def igt_flow(sg, temp_avg, viscosity, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor=1, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate gas flow rate using the IGT (Institute of Gas Technology) formula.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.IGT
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
sg (float): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]
temp_avg (float): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]
viscosity (float): Average viscosity of gas [Pa·s]
length (float): Length of pipe [m]
diameter (float): Diameter of pipe [m]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
comp_factor (float, optional): Average compressibility factor [-] Default is 1.
efficiency (float, optional): Pipeline efficiency factor [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
"""
try:
sg = float(sg)
temp_avg = float(temp_avg)
viscosity = float(viscosity)
length = float(length)
diameter = float(diameter)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if sg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: sg must be positive."
if temp_avg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_avg must be positive."
if viscosity <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: viscosity must be positive."
if length <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: length must be positive."
if diameter <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: diameter must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be non-negative."
if p_outlet >= p_inlet:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be less than p_inlet."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_igt(SG=sg, Tavg=temp_avg, mu=viscosity, L=length, D=diameter,
P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, Zavg=comp_factor, E=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
IS_CHOKED_FLOW
This function checks whether downstream pressure is low enough to produce choked flow for a given upstream pressure and isentropic exponent. It returns a boolean indicating whether sonic conditions are reached at the restriction.
\frac{P_2}{P_1}\le \left(\frac{2}{k+1}\right)^{k/(k-1)}
Excel Usage
=IS_CHOKED_FLOW(p_upstream, p_downstream, k_isentropic)p_upstream(float, required): Higher, source pressure [Pa]p_downstream(float, required): Lower, downstream pressure [Pa]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns (bool): True if flow is choked (critical), False otherwise
Example 1: API 520 Example 1 - not choked
Inputs:
| p_upstream | p_downstream | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|
| 670000 | 532000 | 1.11 |
Excel formula:
=IS_CHOKED_FLOW(670000, 532000, 1.11)Expected output:
false
Example 2: API 520 Example 2 - choked flow
Inputs:
| p_upstream | p_downstream | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|
| 670000 | 101000 | 1.11 |
Excel formula:
=IS_CHOKED_FLOW(670000, 101000, 1.11)Expected output:
true
Example 3: Near critical pressure ratio
Inputs:
| p_upstream | p_downstream | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|
| 1000000 | 500000 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=IS_CHOKED_FLOW(1000000, 500000, 1.4)Expected output:
true
Example 4: High pressure ratio - definitely choked
Inputs:
| p_upstream | p_downstream | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|
| 5000000 | 100000 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=IS_CHOKED_FLOW(5000000, 100000, 1.4)Expected output:
true
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import is_critical_flow as fluids_is_crit
def is_choked_flow(p_upstream, p_downstream, k_isentropic):
"""
Determine if a flow is choked (critical) based on pressure ratio.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.is_critical_flow
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
p_upstream (float): Higher, source pressure [Pa]
p_downstream (float): Lower, downstream pressure [Pa]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns:
bool: True if flow is choked (critical), False otherwise
"""
try:
p_upstream = float(p_upstream)
p_downstream = float(p_downstream)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
if p_upstream <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_upstream must be positive."
if p_downstream < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_downstream must be non-negative."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
if p_downstream >= p_upstream:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_downstream must be less than p_upstream."
result = fluids_is_crit(P1=p_upstream, P2=p_downstream, k=k_isentropic)
return bool(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
ISENTROPIC_EFF
This function converts polytropic efficiency to isentropic efficiency for a specified pressure ratio and heat-capacity ratio. It is used in compressor performance calculations where one efficiency definition is known but the other is required.
\eta_s=\frac{(P_2/P_1)^{(k-1)/k}-1}{(P_2/P_1)^{(k-1)/(k\eta_p)}-1}
Excel Usage
=ISENTROPIC_EFF(p_inlet, p_outlet, k_isentropic, eta_poly)p_inlet(float, required): Initial pressure of gas [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Final pressure of gas [Pa]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]eta_poly(float, required): Polytropic efficiency of the process [-]
Returns (float): Isentropic efficiency calculated from polytropic efficiency [-]
Example 1: 10x compression with 78% polytropic efficiency
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 1000000 | 1.4 | 0.78 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_EFF(100000, 1000000, 1.4, 0.78)Expected output:
0.702761
Example 2: 5x compression with 85% polytropic efficiency
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 500000 | 1.4 | 0.85 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_EFF(100000, 500000, 1.4, 0.85)Expected output:
0.813456
Example 3: High efficiency compressor
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 300000 | 1.3 | 0.92 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_EFF(100000, 300000, 1.3, 0.92)Expected output:
0.909473
Example 4: Different gas (lower k)
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 400000 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_EFF(100000, 400000, 1.2, 0.8)Expected output:
0.776255
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import isentropic_efficiency as fluids_isen_eff
def isentropic_eff(p_inlet, p_outlet, k_isentropic, eta_poly):
"""
Convert between isentropic and polytropic efficiency for compression.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.isentropic_efficiency
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
p_inlet (float): Initial pressure of gas [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Final pressure of gas [Pa]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]
eta_poly (float): Polytropic efficiency of the process [-]
Returns:
float: Isentropic efficiency calculated from polytropic efficiency [-]
"""
try:
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
eta_poly = float(eta_poly)
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be positive."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
if eta_poly <= 0 or eta_poly > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: eta_poly must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_isen_eff(P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, k=k_isentropic, eta_p=eta_poly)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
ISENTROPIC_T_RISE
This function returns the outlet temperature for a gas undergoing isentropic or polytropic compression/expansion, optionally corrected by efficiency. It is useful for estimating thermal loading in compressors and expanders.
T_2=T_1\left[1+\frac{1}{\eta}\left(\left(\frac{P_2}{P_1}\right)^{(k-1)/k}-1\right)\right]
Excel Usage
=ISENTROPIC_T_RISE(temp_init, p_inlet, p_outlet, k_isentropic, efficiency)temp_init(float, required): Initial temperature of gas [K]p_inlet(float, required): Initial pressure of gas [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Final pressure of gas [Pa]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Isentropic efficiency of the process [-]
Returns (float): Final temperature of gas after compression/expansion [K]
Example 1: Compression with 8x pressure ratio
Inputs:
| temp_init | p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 286.8 | 54050 | 432400 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_T_RISE(286.8, 54050, 432400, 1.4)Expected output:
519.523
Example 2: Compression with 80% efficiency
Inputs:
| temp_init | p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 100000 | 500000 | 1.4 | 0.8 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_T_RISE(300, 100000, 500000, 1.4, 0.8)Expected output:
518.932
Example 3: Expansion cooling
Inputs:
| temp_init | p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 1000000 | 100000 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_T_RISE(500, 1000000, 100000, 1.4)Expected output:
258.974
Example 4: Small pressure ratio
Inputs:
| temp_init | p_inlet | p_outlet | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 100000 | 150000 | 1.3 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_T_RISE(300, 100000, 150000, 1.3)Expected output:
329.426
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import isentropic_T_rise_compression as fluids_t_rise
def isentropic_t_rise(temp_init, p_inlet, p_outlet, k_isentropic, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate the temperature rise for isentropic compression or expansion.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.isentropic_T_rise_compression
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
temp_init (float): Initial temperature of gas [K]
p_inlet (float): Initial pressure of gas [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Final pressure of gas [Pa]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]
efficiency (float, optional): Isentropic efficiency of the process [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Final temperature of gas after compression/expansion [K]
"""
try:
temp_init = float(temp_init)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if temp_init <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_init must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be positive."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_t_rise(T1=temp_init, P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, k=k_isentropic, eta=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
ISENTROPIC_WORK
This function computes molar compression/expansion work for an isentropic (or polytropic-style) gas process with optional efficiency correction. Positive values indicate compression work input and negative values indicate expansion.
W=\frac{k}{k-1}ZRT_1\left[\left(\frac{P_2}{P_1}\right)^{(k-1)/k}-1\right]\frac{1}{\eta}
Excel Usage
=ISENTROPIC_WORK(temp_init, k_isentropic, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor, efficiency)temp_init(float, required): Initial temperature of the gas [K]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Compressibility factor of the gas [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Isentropic efficiency of the process [-]
Returns (float): Work performed per mole of gas compressed/expanded [J/mol]
Example 1: Compression with 10x pressure ratio
Inputs:
| temp_init | k_isentropic | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 1.4 | 100000 | 1000000 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_WORK(300, 1.4, 100000, 1000000)Expected output:
8125.16
Example 2: Compression with 78% efficiency
Inputs:
| temp_init | k_isentropic | p_inlet | p_outlet | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 1.4 | 100000 | 1000000 | 0.78 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_WORK(300, 1.4, 100000, 1000000, 0.78)Expected output:
10416.9
Example 3: Expansion (negative work)
Inputs:
| temp_init | k_isentropic | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 1.4 | 1000000 | 100000 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_WORK(300, 1.4, 1000000, 100000)Expected output:
-4208.41
Example 4: Small pressure ratio compression
Inputs:
| temp_init | k_isentropic | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|
| 350 | 1.3 | 100000 | 200000 |
Excel formula:
=ISENTROPIC_WORK(350, 1.3, 100000, 200000)Expected output:
2187.38
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import isentropic_work_compression as fluids_isentropic_work
def isentropic_work(temp_init, k_isentropic, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor=1, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate work of compression or expansion for a gas in an isentropic process.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.isentropic_work_compression
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
temp_init (float): Initial temperature of the gas [K]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
comp_factor (float, optional): Compressibility factor of the gas [-] Default is 1.
efficiency (float, optional): Isentropic efficiency of the process [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Work performed per mole of gas compressed/expanded [J/mol]
"""
try:
temp_init = float(temp_init)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if temp_init <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_init must be positive."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be positive."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_isentropic_work(T1=temp_init, k=k_isentropic, P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, Z=comp_factor, eta=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
ISOTHERMAL_GAS
This function computes mass flow rate for compressible isothermal gas transport in a pipe using pressure-drop, friction, and geometry terms. It is useful for quick steady-state pipeline sizing and operating checks.
\dot m^2=\frac{\left(\frac{\pi D^2}{4}\right)^2\rho(P_1^2-P_2^2)}{P_1\left(f_d\frac{L}{D}+2\ln\frac{P_1}{P_2}\right)}
Excel Usage
=ISOTHERMAL_GAS(rho, fd, p_inlet, p_outlet, length, diameter)rho(float, required): Average density of gas in pipe [kg/m³]fd(float, required): Darcy friction factor [-]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]length(float, required): Length of pipe [m]diameter(float, required): Diameter of pipe [m]
Returns (float): Mass flow rate of gas through pipe [kg/s]
Example 1: Standard gas pipeline flow
Inputs:
| rho | fd | p_inlet | p_outlet | length | diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11.3 | 0.00185 | 1000000 | 900000 | 1000 | 0.5 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_GAS(11.3, 0.00185, 1000000, 900000, 1000, 0.5)Expected output:
145.485
Example 2: High pressure drop case
Inputs:
| rho | fd | p_inlet | p_outlet | length | diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.02 | 2000000 | 1000000 | 5000 | 0.3 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_GAS(10, 0.02, 2000000, 1000000, 5000, 0.3)Expected output:
14.9636
Example 3: Long pipeline with low friction
Inputs:
| rho | fd | p_inlet | p_outlet | length | diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.5 | 0.015 | 5000000 | 4000000 | 50000 | 0.6 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_GAS(8.5, 0.015, 5000000, 4000000, 50000, 0.6)Expected output:
31.2756
Example 4: Small diameter pipe
Inputs:
| rho | fd | p_inlet | p_outlet | length | diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 0.025 | 800000 | 700000 | 100 | 0.1 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_GAS(15, 0.025, 800000, 700000, 100, 0.1)Expected output:
2.62035
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import isothermal_gas as fluids_iso_gas
def isothermal_gas(rho, fd, p_inlet, p_outlet, length, diameter):
"""
Calculate mass flow rate for isothermal compressible gas flow in a pipe.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.isothermal_gas
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
rho (float): Average density of gas in pipe [kg/m³]
fd (float): Darcy friction factor [-]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
length (float): Length of pipe [m]
diameter (float): Diameter of pipe [m]
Returns:
float: Mass flow rate of gas through pipe [kg/s]
"""
try:
rho = float(rho)
fd = float(fd)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
length = float(length)
diameter = float(diameter)
if rho <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: rho must be positive."
if fd <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: fd must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be non-negative."
if p_outlet >= p_inlet:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be less than p_inlet."
if length <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: length must be positive."
if diameter <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: diameter must be positive."
result = fluids_iso_gas(rho=rho, fd=fd, P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, L=length, D=diameter)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
ISOTHERMAL_WORK
This function calculates the ideal isothermal molar work for gas compression or expansion at constant temperature with a compressibility correction. It is a lower-bound work estimate for practical multistage compression systems.
W=ZRT\ln\left(\frac{P_2}{P_1}\right)
Excel Usage
=ISOTHERMAL_WORK(p_inlet, p_outlet, temp, comp_factor)p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]temp(float, required): Temperature of the gas [K]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Compressibility factor of the gas, [-]
Returns (float): Work performed per mole of gas compressed/expanded [J/mol]
Example 1: Compression with 10x pressure ratio
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | temp |
|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 1000000 | 300 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_WORK(100000, 1000000, 300)Expected output:
5743.43
Example 2: Expansion (negative work)
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | temp |
|---|---|---|
| 1000000 | 100000 | 300 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_WORK(1000000, 100000, 300)Expected output:
-5743.43
Example 3: Compression with compressibility factor
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | temp | comp_factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 1000000 | 300 | 0.95 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_WORK(100000, 1000000, 300, 0.95)Expected output:
5456.26
Example 4: Small pressure ratio compression
Inputs:
| p_inlet | p_outlet | temp |
|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 150000 | 350 |
Excel formula:
=ISOTHERMAL_WORK(100000, 150000, 350)Expected output:
1179.93
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import isothermal_work_compression as fluids_isothermal_work
def isothermal_work(p_inlet, p_outlet, temp, comp_factor=1):
"""
Calculate work of compression or expansion for a gas in an isothermal process.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.isothermal_work_compression
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
temp (float): Temperature of the gas [K]
comp_factor (float, optional): Compressibility factor of the gas, [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Work performed per mole of gas compressed/expanded [J/mol]
"""
try:
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
temp = float(temp)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be positive."
if temp <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp must be positive."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
result = fluids_isothermal_work(P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, T=temp, Z=comp_factor)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
MULLER_FLOW
This function estimates gas flow in pipelines with the Muller correlation, which includes viscosity and specific-gravity corrections. It is used for steady operating-point calculations from geometry and pressure conditions.
Q \propto \left(\frac{P_1^2-P_2^2}{L\,Z_{avg}\,T_{avg}}\right)^{0.575}\frac{D^{2.725}}{\mu^{0.15}SG^{0.425}}
Excel Usage
=MULLER_FLOW(sg, temp_avg, viscosity, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor, efficiency)sg(float, required): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]temp_avg(float, required): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]viscosity(float, required): Average viscosity of gas [Pa·s]length(float, required): Length of pipe [m]diameter(float, required): Diameter of pipe [m]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Average compressibility factor [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Pipeline efficiency factor [-]
Returns (float): Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
Example 1: Standard natural gas pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.693 | 277.15 | 0.00001 | 160000 | 0.34 | 9000000 | 2000000 |
Excel formula:
=MULLER_FLOW(0.693, 277.15, 0.00001, 160000, 0.34, 9000000, 2000000)Expected output:
60.458
Example 2: Short pipeline section
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 290 | 0.000012 | 10000 | 0.5 | 5000000 | 4500000 |
Excel formula:
=MULLER_FLOW(0.65, 290, 0.000012, 10000, 0.5, 5000000, 4500000)Expected output:
167.198
Example 3: Pipeline with 92% efficiency
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 280 | 0.00001 | 50000 | 0.4 | 7000000 | 3000000 | 0.92 |
Excel formula:
=MULLER_FLOW(0.7, 280, 0.00001, 50000, 0.4, 7000000, 3000000, 0.92)Expected output:
114.836
Example 4: Large diameter pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | viscosity | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 285 | 0.000011 | 100000 | 1 | 8000000 | 4000000 |
Excel formula:
=MULLER_FLOW(0.6, 285, 0.000011, 100000, 1, 8000000, 4000000)Expected output:
1177.44
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import Muller as fluids_muller
def muller_flow(sg, temp_avg, viscosity, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor=1, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate gas flow rate using the Muller formula.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.Muller
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
sg (float): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]
temp_avg (float): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]
viscosity (float): Average viscosity of gas [Pa·s]
length (float): Length of pipe [m]
diameter (float): Diameter of pipe [m]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
comp_factor (float, optional): Average compressibility factor [-] Default is 1.
efficiency (float, optional): Pipeline efficiency factor [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
"""
try:
sg = float(sg)
temp_avg = float(temp_avg)
viscosity = float(viscosity)
length = float(length)
diameter = float(diameter)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if sg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: sg must be positive."
if temp_avg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_avg must be positive."
if viscosity <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: viscosity must be positive."
if length <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: length must be positive."
if diameter <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: diameter must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be non-negative."
if p_outlet >= p_inlet:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be less than p_inlet."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_muller(SG=sg, Tavg=temp_avg, mu=viscosity, L=length, D=diameter,
P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, Zavg=comp_factor, E=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
P_CRITICAL_FLOW
This function computes the critical static pressure corresponding to Mach 1 from stagnation pressure for an isentropic gas. It is used to evaluate choking limits in nozzles and compressible restrictions.
\frac{P^*}{P_0}=\left(\frac{2}{k+1}\right)^{k/(k-1)}
Excel Usage
=P_CRITICAL_FLOW(p_stag, k_isentropic)p_stag(float, required): Stagnation pressure of a fluid with Ma=1 [Pa]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns (float): Critical flow pressure at Ma=1 [Pa]
Example 1: Textbook example (P=1.4MPa, k=1.289)
Inputs:
| p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 1400000 | 1.289 |
Excel formula:
=P_CRITICAL_FLOW(1400000, 1.289)Expected output:
766813
Example 2: Air at standard conditions (k=1.4)
Inputs:
| p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 500000 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=P_CRITICAL_FLOW(500000, 1.4)Expected output:
264141
Example 3: High pressure nozzle
Inputs:
| p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 5000000 | 1.3 |
Excel formula:
=P_CRITICAL_FLOW(5000000, 1.3)Expected output:
2728640
Example 4: Steam conditions (k=1.135)
Inputs:
| p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 1000000 | 1.135 |
Excel formula:
=P_CRITICAL_FLOW(1000000, 1.135)Expected output:
577430
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import P_critical_flow as fluids_p_crit
def p_critical_flow(p_stag, k_isentropic):
"""
Calculate critical flow pressure for a fluid at Mach 1.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.P_critical_flow
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
p_stag (float): Stagnation pressure of a fluid with Ma=1 [Pa]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns:
float: Critical flow pressure at Ma=1 [Pa]
"""
try:
p_stag = float(p_stag)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
if p_stag <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_stag must be positive."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
result = fluids_p_crit(P=p_stag, k=k_isentropic)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
P_STAGNATION
This function calculates stagnation pressure from static pressure and the static-to-stagnation temperature ratio for an isentropic gas. It is commonly used in compressible-flow diagnostics and nozzle calculations.
\frac{P_0}{P}=\left(\frac{T_0}{T}\right)^{k/(k-1)}
Excel Usage
=P_STAGNATION(pressure, temp, temp_stag, k_isentropic)pressure(float, required): Normal (static) pressure of a fluid [Pa]temp(float, required): Normal (static) temperature of a fluid [K]temp_stag(float, required): Stagnation temperature [K]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns (float): Stagnation pressure [Pa]
Example 1: Textbook example from Cengel
Inputs:
| pressure | temp | temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 54050 | 255.7 | 286.8 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=P_STAGNATION(54050, 255.7, 286.8, 1.4)Expected output:
80772.8
Example 2: High speed flow
Inputs:
| pressure | temp | temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100000 | 250 | 300 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=P_STAGNATION(100000, 250, 300, 1.4)Expected output:
189293
Example 3: Low speed flow (small temperature rise)
Inputs:
| pressure | temp | temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101325 | 290 | 295 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=P_STAGNATION(101325, 290, 295, 1.4)Expected output:
107572
Example 4: Different gas (lower k)
Inputs:
| pressure | temp | temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200000 | 300 | 350 | 1.3 |
Excel formula:
=P_STAGNATION(200000, 300, 350, 1.3)Expected output:
390061
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import P_stagnation as fluids_p_stag
def p_stagnation(pressure, temp, temp_stag, k_isentropic):
"""
Calculate stagnation pressure from static conditions.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.P_stagnation
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
pressure (float): Normal (static) pressure of a fluid [Pa]
temp (float): Normal (static) temperature of a fluid [K]
temp_stag (float): Stagnation temperature [K]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns:
float: Stagnation pressure [Pa]
"""
try:
pressure = float(pressure)
temp = float(temp)
temp_stag = float(temp_stag)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
if pressure <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: pressure must be positive."
if temp <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp must be positive."
if temp_stag <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_stag must be positive."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
if temp_stag < temp:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_stag must be greater than or equal to temp."
result = fluids_p_stag(P=pressure, T=temp, Tst=temp_stag, k=k_isentropic)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
PANHANDLE_A
This function calculates natural-gas pipeline flow with the Panhandle A equation in SI form. It applies an empirical power-law relationship between pressure drop, geometry, gas properties, and throughput.
Q \propto \left(\frac{P_1^2-P_2^2}{L\,SG^{0.8539}\,T_{avg}\,Z_{avg}}\right)^{0.5394}D^{2.6182}
Excel Usage
=PANHANDLE_A(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor, efficiency)sg(float, required): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]temp_avg(float, required): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]length(float, required): Length of pipe [m]diameter(float, required): Diameter of pipe [m]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Average compressibility factor [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Pipeline efficiency factor [-]
Returns (float): Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
Example 1: Standard natural gas pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.693 | 277.15 | 160000 | 0.34 | 9000000 | 2000000 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_A(0.693, 277.15, 160000, 0.34, 9000000, 2000000)Expected output:
46.2618
Example 2: Short pipeline section
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 290 | 10000 | 0.5 | 5000000 | 4500000 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_A(0.65, 290, 10000, 0.5, 5000000, 4500000)Expected output:
126.731
Example 3: Pipeline with 92% efficiency
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 280 | 50000 | 0.4 | 7000000 | 3000000 | 0.92 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_A(0.7, 280, 50000, 0.4, 7000000, 3000000, 0.92)Expected output:
84.8114
Example 4: Large diameter pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 285 | 100000 | 1 | 8000000 | 4000000 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_A(0.6, 285, 100000, 1, 8000000, 4000000)Expected output:
819.552
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import Panhandle_A as fluids_panhandle_a
def panhandle_a(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor=1, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate gas flow rate in a pipeline using the Panhandle A formula.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.Panhandle_A
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
sg (float): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]
temp_avg (float): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]
length (float): Length of pipe [m]
diameter (float): Diameter of pipe [m]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
comp_factor (float, optional): Average compressibility factor [-] Default is 1.
efficiency (float, optional): Pipeline efficiency factor [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
"""
try:
sg = float(sg)
temp_avg = float(temp_avg)
length = float(length)
diameter = float(diameter)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if sg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: sg must be positive."
if temp_avg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_avg must be positive."
if length <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: length must be positive."
if diameter <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: diameter must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be non-negative."
if p_outlet >= p_inlet:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be less than p_inlet."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_panhandle_a(SG=sg, Tavg=temp_avg, L=length, D=diameter,
P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, Zavg=comp_factor, E=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
PANHANDLE_B
This function computes natural-gas flow through pipelines using the Panhandle B correlation. It is similar to Panhandle A but uses a different empirical fit for pressure-drop and diameter dependence.
Q \propto \left(\frac{P_1^2-P_2^2}{L\,SG^{0.961}\,T_{avg}\,Z_{avg}}\right)^{0.51}D^{2.53}
Excel Usage
=PANHANDLE_B(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor, efficiency)sg(float, required): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]temp_avg(float, required): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]length(float, required): Length of pipe [m]diameter(float, required): Diameter of pipe [m]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Average compressibility factor [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Pipeline efficiency factor [-]
Returns (float): Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
Example 1: Standard natural gas pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.693 | 277.15 | 160000 | 0.34 | 9000000 | 2000000 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_B(0.693, 277.15, 160000, 0.34, 9000000, 2000000)Expected output:
46.0366
Example 2: Short pipeline section
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 290 | 10000 | 0.5 | 5000000 | 4500000 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_B(0.65, 290, 10000, 0.5, 5000000, 4500000)Expected output:
122.337
Example 3: Pipeline with 92% efficiency
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 280 | 50000 | 0.4 | 7000000 | 3000000 | 0.92 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_B(0.7, 280, 50000, 0.4, 7000000, 3000000, 0.92)Expected output:
81.9639
Example 4: Large diameter pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 285 | 100000 | 1 | 8000000 | 4000000 |
Excel formula:
=PANHANDLE_B(0.6, 285, 100000, 1, 8000000, 4000000)Expected output:
745.369
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import Panhandle_B as fluids_panhandle_b
def panhandle_b(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor=1, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate gas flow rate in a pipeline using the Panhandle B formula.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.Panhandle_B
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
sg (float): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]
temp_avg (float): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]
length (float): Length of pipe [m]
diameter (float): Diameter of pipe [m]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
comp_factor (float, optional): Average compressibility factor [-] Default is 1.
efficiency (float, optional): Pipeline efficiency factor [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
"""
try:
sg = float(sg)
temp_avg = float(temp_avg)
length = float(length)
diameter = float(diameter)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if sg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: sg must be positive."
if temp_avg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_avg must be positive."
if length <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: length must be positive."
if diameter <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: diameter must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be non-negative."
if p_outlet >= p_inlet:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be less than p_inlet."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_panhandle_b(SG=sg, Tavg=temp_avg, L=length, D=diameter,
P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, Zavg=comp_factor, E=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
POLYTROPIC_EXP
This function computes the polytropic exponent from isentropic exponent and polytropic efficiency for gas compression modeling. It helps map real compressor behavior into a polytropic process representation.
n=\frac{k\eta_p}{1-k(1-\eta_p)}
Excel Usage
=POLYTROPIC_EXP(k_isentropic, eta_poly)k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]eta_poly(float, required): Polytropic efficiency of the process [-]
Returns (float): Polytropic exponent calculated from isentropic exponent and polytropic efficiency [-]
Example 1: Air with 78% polytropic efficiency
Inputs:
| k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|
| 1.4 | 0.78 |
Excel formula:
=POLYTROPIC_EXP(1.4, 0.78)Expected output:
1.57803
Example 2: Air with 85% polytropic efficiency
Inputs:
| k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|
| 1.4 | 0.85 |
Excel formula:
=POLYTROPIC_EXP(1.4, 0.85)Expected output:
1.50633
Example 3: Methane (k=1.3) with 80% efficiency
Inputs:
| k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|
| 1.3 | 0.8 |
Excel formula:
=POLYTROPIC_EXP(1.3, 0.8)Expected output:
1.40541
Example 4: High efficiency at 95%
Inputs:
| k_isentropic | eta_poly |
|---|---|
| 1.4 | 0.95 |
Excel formula:
=POLYTROPIC_EXP(1.4, 0.95)Expected output:
1.43011
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import polytropic_exponent as fluids_poly_exp
def polytropic_exp(k_isentropic, eta_poly):
"""
Calculate polytropic exponent or polytropic efficiency for compression.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.polytropic_exponent
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent of the gas (Cp/Cv) [-]
eta_poly (float): Polytropic efficiency of the process [-]
Returns:
float: Polytropic exponent calculated from isentropic exponent and polytropic efficiency [-]
"""
try:
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
eta_poly = float(eta_poly)
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
if eta_poly <= 0 or eta_poly > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: eta_poly must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_poly_exp(k=k_isentropic, eta_p=eta_poly)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
STAGNATION_ENERGY
This function computes stagnation-energy rise from flow velocity, representing kinetic energy per unit mass available for conversion to enthalpy. It is used in compressible-flow energy balances and total-state calculations.
\Delta h=\frac{V^2}{2}
Excel Usage
=STAGNATION_ENERGY(velocity)velocity(float, required): Velocity of the fluid [m/s]
Returns (float): Increase in enthalpy due to fluid velocity [J/kg]
Example 1: High speed flow (125 m/s)
Inputs:
| velocity |
|---|
| 125 |
Excel formula:
=STAGNATION_ENERGY(125)Expected output:
7812.5
Example 2: Low speed flow (10 m/s)
Inputs:
| velocity |
|---|
| 10 |
Excel formula:
=STAGNATION_ENERGY(10)Expected output:
50
Example 3: Supersonic flow (400 m/s)
Inputs:
| velocity |
|---|
| 400 |
Excel formula:
=STAGNATION_ENERGY(400)Expected output:
80000
Example 4: Subsonic flow (50 m/s)
Inputs:
| velocity |
|---|
| 50 |
Excel formula:
=STAGNATION_ENERGY(50)Expected output:
1250
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import stagnation_energy as fluids_stag_e
def stagnation_energy(velocity):
"""
Calculate the increase in enthalpy due to fluid velocity.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.stagnation_energy
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
velocity (float): Velocity of the fluid [m/s]
Returns:
float: Increase in enthalpy due to fluid velocity [J/kg]
"""
try:
velocity = float(velocity)
if velocity == 0:
return 0.0
result = fluids_stag_e(V=abs(velocity))
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
T_CRITICAL_FLOW
This function computes the critical static temperature for Mach 1 from stagnation temperature for an isentropic gas. It is used with nozzle and choking analyses to determine sonic-state thermodynamic conditions.
\frac{T^*}{T_0}=\frac{2}{k+1}
Excel Usage
=T_CRITICAL_FLOW(temp_stag, k_isentropic)temp_stag(float, required): Stagnation temperature of a fluid with Ma=1 [K]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns (float): Critical flow temperature at Ma=1 [K]
Example 1: Textbook example (T=473K, k=1.289)
Inputs:
| temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 473 | 1.289 |
Excel formula:
=T_CRITICAL_FLOW(473, 1.289)Expected output:
413.281
Example 2: Air at standard conditions (k=1.4)
Inputs:
| temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 300 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=T_CRITICAL_FLOW(300, 1.4)Expected output:
250
Example 3: High temperature nozzle
Inputs:
| temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 800 | 1.3 |
Excel formula:
=T_CRITICAL_FLOW(800, 1.3)Expected output:
695.652
Example 4: Steam conditions (k=1.135)
Inputs:
| temp_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|
| 500 | 1.135 |
Excel formula:
=T_CRITICAL_FLOW(500, 1.135)Expected output:
468.384
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import T_critical_flow as fluids_t_crit
def t_critical_flow(temp_stag, k_isentropic):
"""
Calculate critical flow temperature for a fluid at Mach 1.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.T_critical_flow
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
temp_stag (float): Stagnation temperature of a fluid with Ma=1 [K]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns:
float: Critical flow temperature at Ma=1 [K]
"""
try:
temp_stag = float(temp_stag)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
if temp_stag <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_stag must be positive."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
result = fluids_t_crit(T=temp_stag, k=k_isentropic)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
T_STAG_IDEAL
This function returns ideal stagnation temperature from static temperature, velocity, and constant-pressure heat capacity. It models conversion of kinetic energy into thermal energy in adiabatic deceleration.
T_0=T+\frac{V^2}{2C_p}
Excel Usage
=T_STAG_IDEAL(temp, velocity, cp)temp(float, required): Static temperature [K]velocity(float, required): Velocity [m/s]cp(float, required): Heat capacity at constant pressure [J/kg/K]
Returns (float): Stagnation temperature [K]
Example 1: Textbook example from Cengel
Inputs:
| temp | velocity | cp |
|---|---|---|
| 255.7 | 250 | 1005 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAG_IDEAL(255.7, 250, 1005)Expected output:
286.795
Example 2: High speed aircraft
Inputs:
| temp | velocity | cp |
|---|---|---|
| 220 | 300 | 1005 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAG_IDEAL(220, 300, 1005)Expected output:
264.776
Example 3: Low speed flow
Inputs:
| temp | velocity | cp |
|---|---|---|
| 300 | 50 | 1005 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAG_IDEAL(300, 50, 1005)Expected output:
301.244
Example 4: Different gas (helium, high Cp)
Inputs:
| temp | velocity | cp |
|---|---|---|
| 300 | 200 | 5193 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAG_IDEAL(300, 200, 5193)Expected output:
303.851
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import T_stagnation_ideal as fluids_t_stag_ideal
def t_stag_ideal(temp, velocity, cp):
"""
Calculate ideal stagnation temperature from velocity and heat capacity.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.T_stagnation_ideal
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
temp (float): Static temperature [K]
velocity (float): Velocity [m/s]
cp (float): Heat capacity at constant pressure [J/kg/K]
Returns:
float: Stagnation temperature [K]
"""
try:
temp = float(temp)
velocity = float(velocity)
cp = float(cp)
if temp <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp must be positive."
if cp <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: cp must be positive."
result = fluids_t_stag_ideal(T=temp, V=velocity, Cp=cp)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
T_STAGNATION
This function computes stagnation temperature from static temperature and pressure ratio under isentropic assumptions. It is useful when recovering total temperature from measured static flow conditions.
T_0=T\left(\frac{P_0}{P}\right)^{(k-1)/k}
Excel Usage
=T_STAGNATION(temp, pressure, p_stag, k_isentropic)temp(float, required): Normal (static) temperature of a fluid [K]pressure(float, required): Normal (static) pressure of a fluid [Pa]p_stag(float, required): Stagnation pressure [Pa]k_isentropic(float, required): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns (float): Stagnation temperature [K]
Example 1: Textbook example from Cengel
Inputs:
| temp | pressure | p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 286.8 | 54050 | 432400 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAGNATION(286.8, 54050, 432400, 1.4)Expected output:
519.523
Example 2: High speed flow
Inputs:
| temp | pressure | p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 50000 | 100000 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAGNATION(250, 50000, 100000, 1.4)Expected output:
304.753
Example 3: Low speed flow (small pressure rise)
Inputs:
| temp | pressure | p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 100000 | 110000 | 1.4 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAGNATION(300, 100000, 110000, 1.4)Expected output:
308.282
Example 4: Different gas (lower k)
Inputs:
| temp | pressure | p_stag | k_isentropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| 320 | 200000 | 400000 | 1.3 |
Excel formula:
=T_STAGNATION(320, 200000, 400000, 1.3)Expected output:
375.507
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import T_stagnation as fluids_t_stag
def t_stagnation(temp, pressure, p_stag, k_isentropic):
"""
Calculate stagnation temperature from pressure ratio.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.T_stagnation
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
temp (float): Normal (static) temperature of a fluid [K]
pressure (float): Normal (static) pressure of a fluid [Pa]
p_stag (float): Stagnation pressure [Pa]
k_isentropic (float): Isentropic exponent [-]
Returns:
float: Stagnation temperature [K]
"""
try:
temp = float(temp)
pressure = float(pressure)
p_stag = float(p_stag)
k_isentropic = float(k_isentropic)
if temp <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp must be positive."
if pressure <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: pressure must be positive."
if p_stag <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_stag must be positive."
if k_isentropic <= 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: k_isentropic must be greater than 1."
if p_stag < pressure:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_stag must be greater than or equal to pressure."
result = fluids_t_stag(T=temp, P=pressure, Pst=p_stag, k=k_isentropic)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator
WEYMOUTH_FLOW
This function estimates compressible-gas pipeline flow with the Weymouth equation under steady-state assumptions. It relates volumetric flow to pressure drop, pipe size, and gas thermophysical corrections.
Q \propto \left(\frac{P_1^2-P_2^2}{L\,SG\,T_{avg}\,Z_{avg}}\right)^{1/2}D^{2.667}
Excel Usage
=WEYMOUTH_FLOW(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor, efficiency)sg(float, required): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]temp_avg(float, required): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]length(float, required): Length of pipe [m]diameter(float, required): Diameter of pipe [m]p_inlet(float, required): Inlet pressure [Pa]p_outlet(float, required): Outlet pressure [Pa]comp_factor(float, optional, default: 1): Average compressibility factor [-]efficiency(float, optional, default: 1): Pipeline efficiency factor [-]
Returns (float): Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
Example 1: Standard natural gas pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.693 | 277.15 | 160000 | 0.34 | 9000000 | 2000000 |
Excel formula:
=WEYMOUTH_FLOW(0.693, 277.15, 160000, 0.34, 9000000, 2000000)Expected output:
34.8666
Example 2: Short pipeline section
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 290 | 10000 | 0.5 | 5000000 | 4500000 |
Excel formula:
=WEYMOUTH_FLOW(0.65, 290, 10000, 0.5, 5000000, 4500000)Expected output:
97.7999
Example 3: Pipeline with 92% efficiency
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet | efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 280 | 50000 | 0.4 | 7000000 | 3000000 | 0.92 |
Excel formula:
=WEYMOUTH_FLOW(0.7, 280, 50000, 0.4, 7000000, 3000000, 0.92)Expected output:
63.1529
Example 4: Large diameter pipeline
Inputs:
| sg | temp_avg | length | diameter | p_inlet | p_outlet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 285 | 100000 | 1 | 8000000 | 4000000 |
Excel formula:
=WEYMOUTH_FLOW(0.6, 285, 100000, 1, 8000000, 4000000)Expected output:
655.567
Python Code
Show Code
from fluids.compressible import Weymouth as fluids_weymouth
def weymouth_flow(sg, temp_avg, length, diameter, p_inlet, p_outlet, comp_factor=1, efficiency=1):
"""
Calculate gas flow rate in a pipeline using the Weymouth formula.
See: https://fluids.readthedocs.io/fluids.compressible.html#fluids.compressible.Weymouth
This example function is provided as-is without any representation of accuracy.
Args:
sg (float): Specific gravity of gas relative to air [-]
temp_avg (float): Average temperature of gas in pipeline [K]
length (float): Length of pipe [m]
diameter (float): Diameter of pipe [m]
p_inlet (float): Inlet pressure [Pa]
p_outlet (float): Outlet pressure [Pa]
comp_factor (float, optional): Average compressibility factor [-] Default is 1.
efficiency (float, optional): Pipeline efficiency factor [-] Default is 1.
Returns:
float: Gas flow rate at reference conditions [m³/s]
"""
try:
sg = float(sg)
temp_avg = float(temp_avg)
length = float(length)
diameter = float(diameter)
p_inlet = float(p_inlet)
p_outlet = float(p_outlet)
comp_factor = float(comp_factor)
efficiency = float(efficiency)
if sg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: sg must be positive."
if temp_avg <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: temp_avg must be positive."
if length <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: length must be positive."
if diameter <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: diameter must be positive."
if p_inlet <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_inlet must be positive."
if p_outlet < 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be non-negative."
if p_outlet >= p_inlet:
return "Error: Invalid input: p_outlet must be less than p_inlet."
if comp_factor <= 0:
return "Error: Invalid input: comp_factor must be positive."
if efficiency <= 0 or efficiency > 1:
return "Error: Invalid input: efficiency must be between 0 and 1."
result = fluids_weymouth(SG=sg, Tavg=temp_avg, L=length, D=diameter,
P1=p_inlet, P2=p_outlet, Zavg=comp_factor, E=efficiency)
return float(result)
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}"Online Calculator