Overview
Mathematical computation forms the backbone of quantitative analysis in science, engineering, finance, and data science. This comprehensive library of mathematical functions extends Excel’s capabilities far beyond native formulas, providing access to sophisticated numerical methods implemented in SciPy, NumPy, CasADi, and specialized Python libraries.
Modern mathematical computing requires far more than basic arithmetic—it demands robust algorithms for solving differential equations, fitting complex models to data, optimizing multivariate functions, and performing matrix operations with numerical stability. These functions bridge the gap between Excel’s spreadsheet interface and the power of production-grade scientific computing libraries, enabling researchers and engineers to tackle challenging mathematical problems directly from within a familiar spreadsheet environment.
Calculus and Differential Equations form the foundation for modeling dynamic systems. Whether computing derivatives of multivariable functions through differentiation, evaluating integrals numerically, or solving systems of ordinary differential equations, these tools enable accurate analysis of continuous change. Applications range from sensitivity analysis in optimization to pharmacokinetic modeling in drug development and epidemic modeling in public health.
Curve Fitting and Data Approximation allow you to discover the relationships hidden within data. Using least-squares regression, you can fit symbolic models or pre-defined curves to experimental measurements. This is essential across fields: chemists use adsorption and binding models to understand molecular interactions; biologists apply dose-response and enzyme kinetics models; engineers work with rheological and spectroscopic models. Advanced methods like CasADi-based fitting provide automatic differentiation for complex symbolic expressions, while spline-based interpolation reconstructs smooth curves from scattered or structured data.
Interpolation and Approximation bridge discrete data points with smooth continuous functions. Methods range from simple univariate splines and polynomial interpolation to sophisticated multidimensional approaches like radial basis functions. These are invaluable when you need to evaluate functions at arbitrary points, smooth noisy measurements, or reconstruct surfaces from scattered measurements.
Linear Algebra provides the computational foundation for modern numerical analysis. From matrix decompositions (QR, SVD, Cholesky) to solving linear systems and pseudoinverse computations, these operations underpin virtually every scientific computation. They are essential for solving overdetermined and underdetermined systems, analyzing system stability through eigenvalue problems, and transforming data for machine learning applications.
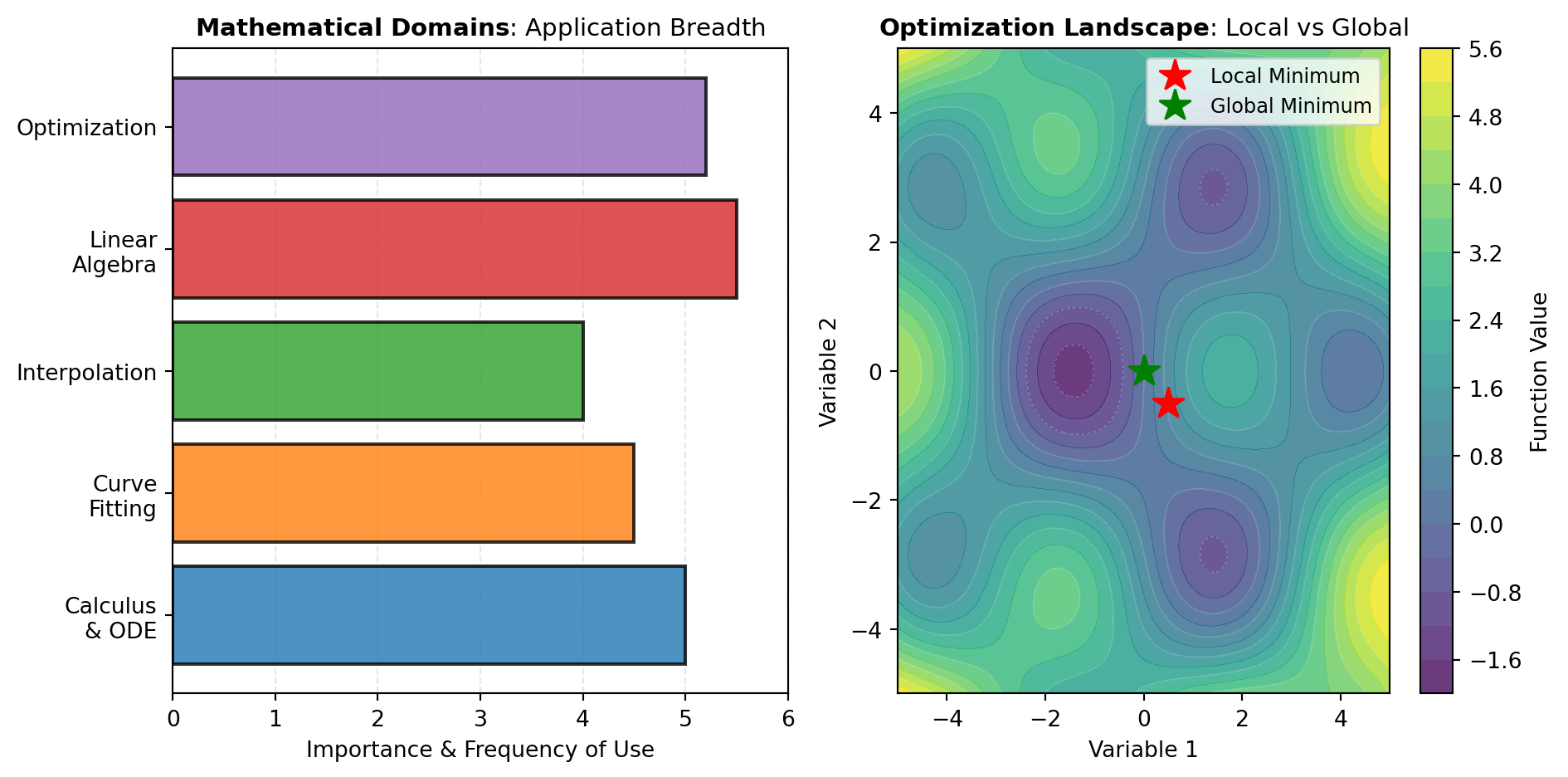
Optimization addresses the central computational challenge: finding the best solution within constraints. Assignment problems like the Hungarian algorithm match resources optimally. Local methods converge rapidly near a solution, suitable when good starting points are available. Global methods like differential evolution and dual annealing explore broader solution spaces to escape local minima. Linear and quadratic programming handle structured problems efficiently, while root-finding tools solve systems of nonlinear equations that arise throughout engineering and science. The reference figure illustrates these key mathematical domains and their interconnections.
Calculus
Differentiation
| HESSIAN |
Compute the Hessian matrix (second derivatives) of a scalar function using CasADi symbolic differentiation. |
| JACOBIAN |
Calculate the Jacobian matrix of mathematical expressions with respect to specified variables. |
| SENSITIVITY |
Compute the sensitivity of a scalar model with respect to its parameters using CasADi. |
Integration
| DBLQUAD |
Compute the double integral of a function over a two-dimensional region. |
| QUAD |
Numerically integrate a function defined by a table of x, y values over [a, b] using adaptive quadrature. |
| TRAPEZOID |
Integrate sampled data using the composite trapezoidal rule. |
Ode Models
| BRUSSELATOR |
Numerically solves the Brusselator system of ordinary differential equations for autocatalytic chemical reactions. |
| COMPARTMENTAL_PK |
Numerically solves the basic one-compartment pharmacokinetics ODE using scipy.integrate.solve_ivp. |
| FITZHUGH_NAGUMO |
Numerically solves the FitzHugh-Nagumo system of ordinary differential equations for neuron action potentials using scipy.integrate.solve_ivp. |
| HODGKIN_HUXLEY |
Numerically solves the Hodgkin-Huxley system of ordinary differential equations for neuron action potentials. |
| LORENZ |
Numerically solves the Lorenz system of ordinary differential equations for chaotic dynamics. |
| LOTKA_VOLTERRA |
Numerically solves the Lotka-Volterra predator-prey system of ordinary differential equations. |
| MICHAELIS_MENTEN |
Numerically solves the Michaelis-Menten system of ordinary differential equations for enzyme kinetics using scipy.integrate.solve_ivp. |
| SEIR |
Numerically solves the SEIR system of ordinary differential equations for infectious disease modeling using scipy.integrate.solve_ivp. |
| SIR |
Solves the SIR system of ordinary differential equations for infection dynamics using scipy.integrate.solve_ivp (see scipy.integrate.solve_ivp). |
| VAN_DER_POL |
Numerically solves the Van der Pol oscillator system of ordinary differential equations. |
Ode Systems
| SOLVE_BVP |
Solve a boundary value problem for a second-order system of ODEs. |
| SOLVE_IVP |
Solve an initial value problem for a system of ODEs of the form dy/dt = A @ y. |
Curve Fitting
Least Squares
| CA_CURVE_FIT |
Fit an arbitrary symbolic model to data using CasADi and automatic differentiation. |
| CURVE_FIT |
Fit a model expression to xdata, ydata using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| LM_FIT |
Fit data using lmfit’s built-in models with optional model composition. |
| MINUIT_FIT |
Fit an arbitrary model expression to data using iminuit least-squares minimization with uncertainty estimates. |
Models
| ADSORPTION |
Fits adsorption models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| AGRICULTURE |
Fits agriculture models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| BINDING_MODEL |
Fits binding_model models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| CHROMA_PEAKS |
Fits chroma_peaks models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| DOSE_RESPONSE |
Fits dose_response models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| ELECTRO_ION |
Fits electro_ion models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| ENZYME_BASIC |
Fits enzyme_basic models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| ENZYME_INHIBIT |
Fits enzyme_inhibit models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| EXP_ADVANCED |
Fits exp_advanced models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| EXP_DECAY |
Fits exp_decay models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| EXP_GROWTH |
Fits exponential growth models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| GROWTH_POWER |
Fits growth_power models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| GROWTH_SIGMOID |
Fits growth_sigmoid models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| MISC_PIECEWISE |
Fits misc_piecewise models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| PEAK_ASYM |
Fits peak_asym models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| POLY_BASIC |
Fits poly_basic models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| RHEOLOGY |
Fits rheology models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| SPECTRO_PEAKS |
Fits spectro_peaks models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| STAT_DISTRIB |
Fits stat_distrib models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| STAT_PARETO |
Fits stat_pareto models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
| WAVEFORM |
Fits waveform models to data using scipy.optimize.curve_fit. |
Geometry
Triangle Solvers
| TRI_AAAS |
Solve a triangle from three angles and one side for scale. |
| TRI_SAS |
Solve a triangle from two sides and their included angle. |
| TRI_SOLVE |
Solve a triangle from any valid combination of three known side/angle values. |
| TRI_SSA |
Solve a triangle from two sides and a non-included angle using SSA branch selection. |
| TRI_SSS |
Solve a triangle from three known side lengths. |
Trig Identities
| TRIG_EXPAND |
Expand trigonometric compound-angle expressions into component terms. |
| TRIG_FU |
Simplify trigonometric expressions using the Fu transformation pipeline. |
| TRIG_TR1 |
Rewrite secant and cosecant into reciprocal cosine and sine forms. |
| TRIG_TR10 |
Expand sine and cosine of summed angles into separated component terms. |
| TRIG_TR2 |
Rewrite tangent and cotangent into sine-cosine ratio forms. |
| TRIG_TR3 |
Normalize trig signs and induced odd/even identity forms. |
| TRIG_TR4 |
Evaluate exact trigonometric values at standard special angles. |
| TRIG_TR5 |
Replace even powers of sine using a cosine-based identity. |
| TRIG_TR6 |
Replace even powers of cosine using a sine-based identity. |
| TRIG_TR7 |
Apply power-reduction to cosine-squared terms. |
| TRIG_TR8 |
Convert products of sine and cosine terms into sum or difference forms. |
| TRIG_TR9 |
Convert sums of sine or cosine terms into product forms. |
| TRIG_TRIGSIMP |
Simplify a trigonometric expression using identity transformations. |
Graph Theory
Shortest Path
| MIN_SPANNING_TREE |
Find the minimum spanning tree (MST) of an undirected graph. |
| SHORTEST_PATH |
Find the shortest path and its length between two nodes in a network. |
Interpolation
Approximation
| LAGRANGE_INTERP |
Compute the Lagrange interpolating polynomial through a set of points. |
| PADE |
Compute Pade rational approximation to a polynomial. |
Linear Algebra
Decompositions
| CHOLESKY |
Compute the Cholesky decomposition of a real, symmetric positive-definite matrix. |
| HESSENBERG |
Compute Hessenberg form of a matrix. |
| LDL |
Compute the LDLt or Bunch-Kaufman factorization of a symmetric matrix. |
| LU |
Compute LU decomposition of a matrix with partial pivoting. |
| POLAR |
Compute the polar decomposition of a matrix. |
| QR |
Compute the QR decomposition of a matrix and return either Q or R. |
| SCHUR |
Compute Schur decomposition of a matrix. |
| SVD |
Compute the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of a matrix using scipy.linalg.svd. |
Eigenvalues
| EIG |
Compute eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a general square matrix. |
| EIGH |
Solve eigenvalue problem for a real symmetric or complex Hermitian matrix. |
| EIGVALS |
Compute eigenvalues of a general square matrix. |
| EIGVALSH |
Compute eigenvalues of a real symmetric or complex Hermitian matrix. |
Equations
| LSQ_LINEAR |
Solve a bounded linear least-squares problem. |
| LSTSQ |
Compute the least-squares solution to Ax = B using scipy.linalg.lstsq. |
| SOLVE |
Solve a linear matrix equation, or system of linear scalar equations. |
| SOLVE_BANDED |
Solve the equation Ax = b for x, assuming A is a banded matrix. |
| SOLVE_TOEPLITZ |
Solve a Toeplitz system using Levinson Recursion. |
| SOLVE_TRIANGULAR |
Solve the equation Ax = b for x, assuming A is a triangular matrix. |
Matrix Functions
| COSM |
Compute the matrix cosine. |
| EXPM |
Compute the matrix exponential of a square matrix using scipy.linalg.expm |
| FRAC_MAT_POW |
Compute the fractional power of a square matrix. |
| LOGM |
Compute matrix logarithm. |
| SINM |
Compute the matrix sine. |
| SQRTM |
Compute the matrix square root. |
Matrix Operations
| DET |
Compute the determinant of a square matrix. |
| INV |
Compute the inverse of a square matrix. |
| KHATRI_RAO |
Compute the Khatri-Rao product of two matrices. |
| KRON |
Compute the Kronecker product of two matrices. |
| MATRIX_NORM |
Compute matrix or vector norm. |
| PINV |
Compute the Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse of a matrix using singular value decomposition (SVD). |
Number Theory
Gcd Lcm Divisors
| DIVCOUNT |
Count divisors of an integer with optional modulus filtering. |
| DIVISORS |
List divisors of an integer with optional proper divisor mode. |
| GCD |
Compute the greatest common divisor of one or more integers. |
| ISQRT |
Compute the integer square root of a nonnegative integer. |
| LCM |
Compute the least common multiple of one or more integers. |
| PPY_PHI |
Compute Euler’s totient function using the primePy implementation. |
| PROPDIVCNT |
Count proper divisors of an integer with optional modulus filtering. |
| PROPDIVS |
List proper divisors of an integer. |
| REDUCEDTOT |
Compute Carmichael’s reduced totient function for an integer. |
| TOTIENT |
Compute Euler’s totient function for an integer. |
Modular Arithmetic
| DLOG |
Solve discrete logarithms in modular arithmetic. |
| ISPRIMROOT |
Check whether a value is a primitive root modulo n. |
| ISQUADRES |
Check whether a value is a quadratic residue modulo p. |
| JACOBI |
Compute the Jacobi symbol for two integers. |
| LEGENDRE |
Compute the Legendre symbol modulo an odd prime. |
| NORDER |
Find the multiplicative order of an integer modulo n. |
| NTHROOTMOD |
Solve nth-power congruences modulo an integer. |
| PRIMROOT |
Find a primitive root modulo n when one exists. |
| QUADCONG |
Solve quadratic congruences modulo n. |
| QUADRES |
List all quadratic residues modulo p. |
| SQRTMOD |
Solve quadratic congruences of the form x squared congruent to a. |
Prime Numbers
| FACTORINT |
Compute the prime factorization of an integer with multiplicities. |
| ISPRIME |
Determine whether an integer is prime. |
| NEXTPRIME |
Return the ith prime number greater than a given integer. |
| PPY_PRIMEBETWEEN |
List prime numbers between two bounds using primePy. |
| PPY_PRIMECHECK |
Check primality using the primePy implementation. |
| PPY_PRIMEUPTO |
List all prime numbers up to a maximum value using primePy. |
| PREVPRIME |
Return the largest prime smaller than a given integer. |
| PRIME |
Return the nth prime number. |
| PRIMEFACTORS |
Return distinct prime factors of an integer. |
| PRIMEPI |
Count the number of primes less than or equal to an integer. |
| PRIMERANGE |
Generate all prime numbers in a specified interval. |
| RANDPRIME |
Sample a prime number from a half-open integer interval. |
Optimization
Assignment Problems
| LINEAR_ASSIGNMENT |
Solve the linear assignment problem using scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment. |
| QUAD_ASSIGN |
Solve a quadratic assignment problem using SciPy’s implementation. |
Global Optimization
| BASIN_HOPPING |
Minimize a single-variable expression with SciPy’s basinhopping algorithm. |
| BRUTE |
Perform a brute-force grid search to approximate the global minimum of a function. |
| DIFF_EVOLUTION |
Minimize a multivariate function using differential evolution. |
| DUAL_ANNEALING |
Minimize a multivariate function using dual annealing. |
| SHGO |
Find global minimum using Simplicial Homology Global Optimization. |
Linear Programming
| CA_QUAD_PROG |
Solve a quadratic programming problem using CasADi’s qpsol solver. |
| LINEAR_PROG |
Solve a linear programming problem using SciPy’s linprog function. |
| MILP |
Solve a mixed-integer linear program using scipy.optimize.milp. |
Local Optimization
| CA_MINIMIZE |
Minimize a multivariate function using CasADi with automatic differentiation. |
| MINIMIZE |
Minimize a multivariate function using SciPy’s minimize routine. |
| MINIMIZE_SCALAR |
Minimize a single-variable function using SciPy’s minimize_scalar. |
Root Finding
| CA_ROOT |
Solve a system of nonlinear equations using CasADi with automatic Jacobian. |
| FIXED_POINT |
Find a fixed point x such that f(x) = x for a scalar function expression. |
| ROOT |
Solve a square nonlinear system using SciPy’s root solver. |
| ROOT_SCALAR |
Find a real root of a scalar function using SciPy’s root_scalar. |
Special Functions
Bessel Functions
| BESSEL_HANKEL1 |
Compute the cylindrical Hankel function of the first kind and return real and imaginary parts. |
| BESSEL_HANKEL2 |
Compute the cylindrical Hankel function of the second kind and return real and imaginary parts. |
| BESSEL_IV |
Compute the modified cylindrical Bessel function of the first kind for real order. |
| BESSEL_JN_ZEROS |
Compute the first positive zeros of the integer-order Bessel function of the first kind. |
| BESSEL_JV |
Compute the cylindrical Bessel function of the first kind for real order. |
| BESSEL_KV |
Compute the modified cylindrical Bessel function of the second kind for real order. |
| BESSEL_YN_ZEROS |
Compute the first positive zeros of the integer-order Bessel function of the second kind. |
| BESSEL_YV |
Compute the cylindrical Bessel function of the second kind for real order. |
| SPHERICAL_IN |
Compute the modified spherical Bessel function of the first kind or its derivative. |
| SPHERICAL_JN |
Compute the spherical Bessel function of the first kind or its derivative. |
| SPHERICAL_KN |
Compute the modified spherical Bessel function of the second kind or its derivative. |
| SPHERICAL_YN |
Compute the spherical Bessel function of the second kind or its derivative. |
Elliptic Integrals
| ELLIPE |
Compute the complete elliptic integral of the second kind. |
| ELLIPEINC |
Compute the incomplete elliptic integral of the second kind. |
| ELLIPJ |
Compute Jacobi elliptic functions sn, cn, dn and amplitude for scalar input. |
| ELLIPK |
Compute the complete elliptic integral of the first kind. |
| ELLIPKINC |
Compute the incomplete elliptic integral of the first kind. |
| ELLIPKM1 |
Compute the complete elliptic integral of the first kind near m equals one. |
| ELLIPRC |
Compute Carlson’s degenerate symmetric elliptic integral RC. |
| ELLIPRD |
Compute Carlson’s symmetric elliptic integral RD. |
| ELLIPRF |
Compute Carlson’s completely symmetric elliptic integral RF. |
| ELLIPRG |
Compute Carlson’s completely symmetric elliptic integral RG. |
| ELLIPRJ |
Compute Carlson’s symmetric elliptic integral RJ. |
Error And Fresnel
| DAWSN |
Evaluate Dawson’s integral for a real input. |
| ERF |
Evaluate the Gauss error function for a real input. |
| ERFC |
Evaluate the complementary error function for a real input. |
| ERFCINV |
Compute the inverse complementary error function on its real domain. |
| ERFCX |
Evaluate the exponentially scaled complementary error function. |
| ERFI |
Evaluate the imaginary error function for a real input. |
| ERFINV |
Compute the inverse error function on its real domain. |
| FRESNEL |
Compute Fresnel sine and cosine integrals for a real input. |
| WOFZ |
Compute the Faddeeva function and return real and imaginary parts. |
Gamma Beta Functions
| BETAINC |
Compute the regularized incomplete beta function. |
| BETAINCINV |
Invert the regularized incomplete beta function with respect to x. |
| BETALN |
Compute the natural logarithm of the absolute beta function. |
| DIGAMMA |
Compute the digamma function for a real input. |
| EULER_BETA |
Evaluate the Euler beta function for two real parameters. |
| GAMMA |
Evaluate the gamma function for a real input. |
| GAMMAINC |
Compute the regularized lower incomplete gamma function. |
| GAMMAINCC |
Compute the regularized upper incomplete gamma function. |
| GAMMAINCCINV |
Invert the regularized upper incomplete gamma function. |
| GAMMAINCINV |
Invert the regularized lower incomplete gamma function. |
| GAMMALN |
Compute the natural logarithm of the absolute gamma function. |
| POCH |
Evaluate the rising factorial using the Pochhammer symbol. |
| POLYGAMMA |
Compute the n-th derivative of the digamma function. |
| RGAMMA |
Compute the reciprocal of the gamma function. |